Reinforcement
Introduction
Dental disorders are the most common human diseases. Worldwide, 60-90% of school-aged children and almost 100% of adult population have dental caries. In addition, 30% of the world population aged 65-74 suffer from completely absent dentition (secondary edentulism). Governments and private companies allocate considerable amounts of funds for scientific and clinical research; they found institutes where numerous theses are defended. However, the complications in conventional dentistry do not decrease drastically. Thus, in case of conventinal treatment, dentistry keeps the leading place by the number of issues that inevitably lead to short- and long-term complications.
A physician uses legislatively approved materials and technologies in treatment and prosthetics. In most cases, the inevitable complications arise through no dentist's fault. The main paradox is that the dentists are only people legitimately responsible for these complications.
The dental revolution of the mid-20th century is creation of composite materials on the matrix basis developed by Rafael L. Bowen. Bowen's resin and other different fillers formed a category of widely used composite materials with excellent technological and physico-chemical properties. Their emergence gave rise to the composite tooth restoration. Dental treatment by sparing minimally invasive methods became possible. The minimally aggressive dental treatment, with its "systematic care for the original tissue," is a relatively new trend in dentistry. Progressive dentistry recognizes the following: an artificial structure has less biological value than the original healthy dental tissue does. The first World Congress of Minimally Invasive Dentistry (WCMID) noted this new trend as promising. In fact, the non-invasive treatment is still not widely used in dental practice. In conventional treatment and prosthetics methods, teeth are prepared for particular structures. Traumatic and aggressive preparation is carried out. Not only demineralized but also healthy solid tissues are removed. Elimination of the healthy dental tissues, especially the enamel, makes them less resistant, weaker, and leads to their destruction.
Almost 100 million teeth, totaling up to 5 billion dollars, are restored in the United States using the composite materials. Composite materials today represent a baseground for progressive restorative dentistry. Restoration and correction of functional and esthetic tooth parameters and the tooth row for three decades enabled us to thoroughly study the opportunities created by this class of restoration materials.
Though having definite advantages, these materials are not perfect. Working on their drawbacks and on reduction in complications enabled us to identify the main reasons for the composite restoration complications and, accordingly, to propose a number of innovations. Our team was able to significantly expand the range of the composite material application and developed unique combinations of their use.
7 most common root causes resulting in occurence of different complications after the traditional techniques of removing defects of hard tooth tissues and dental arch were identified:
- use of artificial materials;
- traumatic or aggressive preparation of hard tooth tissues;
- extraction of the neurovascular bundle (pulp removal) for a specific restoration;
- tooth restoration without taking into account design, anatomical-topographic and biomechanical features;
- use of crowns;
- use of pin-type configurations;
- lack of systemic approach to rendering tooth's care.
To minimize complications and to extend the active functioning period of restored teeth and teeth rows, the innovativemethods in dentistry, unique in the world, were developed and patented:
- tooth restoration/reconstruction and prosthetics sing the reinforced mesh metallocomposite (MMC) that meet the MIPS (Minimal Invasion with Pulp Save) concept under M. Melikian;
- mechanical activation of composite materials: manual, vibration, manual/vibration;
- the concept of no-anesthesia tooth preparation;
- concept of thermal balance in case of layered composite tooth restoration under M.L. Melikian;
- GibTon concept: exclusive tools for layered mechano-activated tooth restoration in the balanced temperature conditions.
Reinforcement of composite materials By M. Melikian
Reinforcement, armoring (from Latin armo - to arm, to strengthen) is strengthening of a material or a structure with elements made of a stronger material (e.g. metallic grid or wire).
The lacune of covering of the reinforcement in medicine in literary sources forced us to study it in other fields. For instance, reinforcement has a long history of use in construction. It is enough to say that all structures are reinforced now, and the strength of a reinforced beam increases by 15-20 times as compared with a concrete (non-reinforced) one.
To eliminate defects in composite materials, we first applied the reinforcing element as a mesh. The mesh can be metalic or non-metallic.
Reinforcement of composite restoration by M. Melikian is the optimal location of a metal of non-metal element in the composite material in the process of treatment, restoration/reconstruction or prosthodontics with allowance made for anatomically topographic and biomechanical features of the tooth structure, which mitigates shortcomings of the composite material, reduces or eliminates number of complications, increases functioning period of the composite restoration.
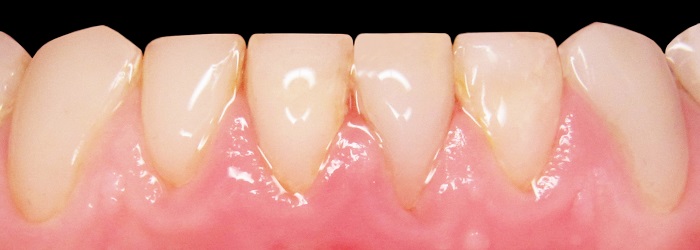
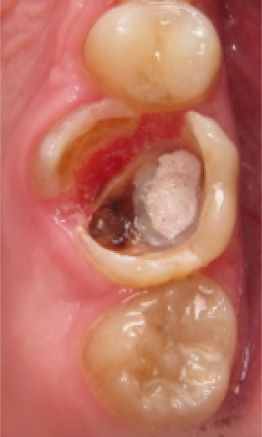
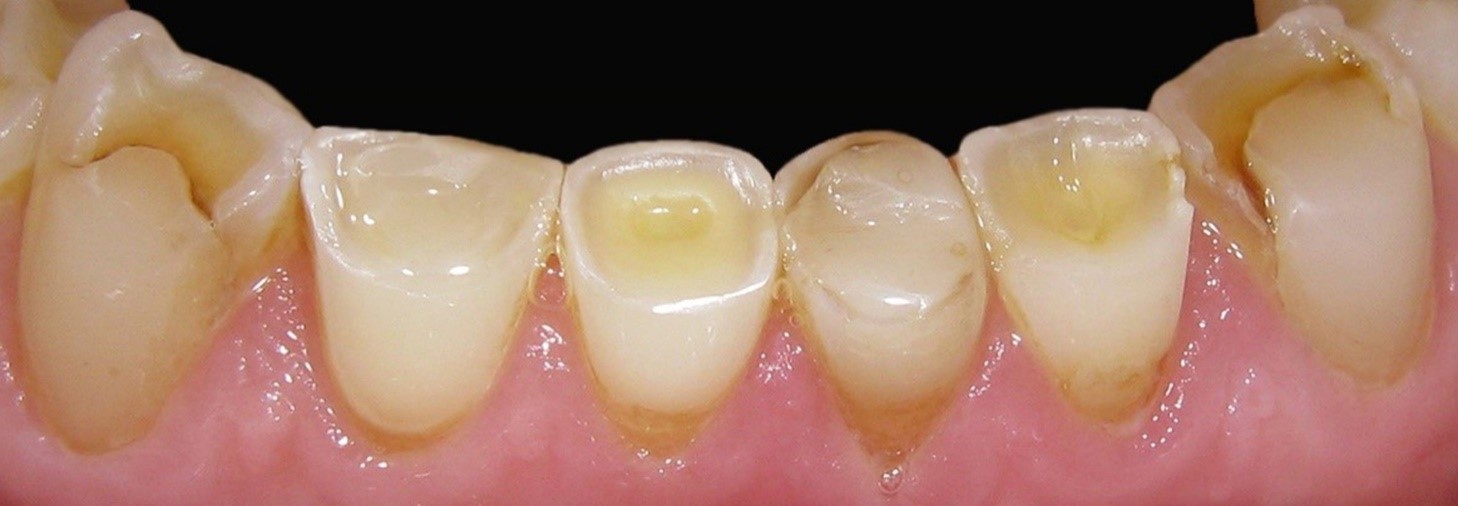
before
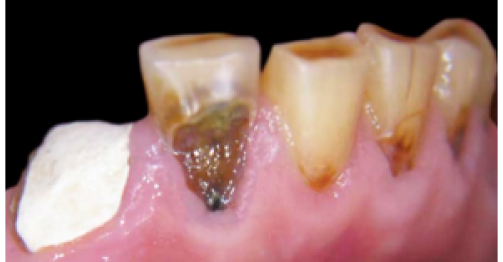
in work
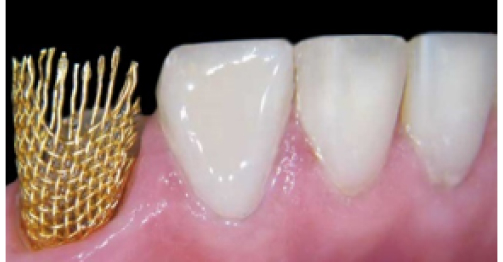
after
The essence of the innovative non-traumatic technology is in the fact that, irrespective of the clinical situation, tooth or tooth row defects are eliminated after gentle preparation. Destroyed and demineralized tissues are only dissected during preparation. The reinforcing structure is manufactured, and after its fitting, adjustment and fixation, the defect is eliminated using composite materials.
The grid, after fixing, seats inside the composite restoration in isolated state, not in direct contact with the hard tooth tissues, gum, bio-fluid of oral cavity and antagonistic teeth.
The combination of composites and metallic mesh resulted in creation of the mesh metallic composites (MMC), the properties of which are entirely different from the properties of its components.
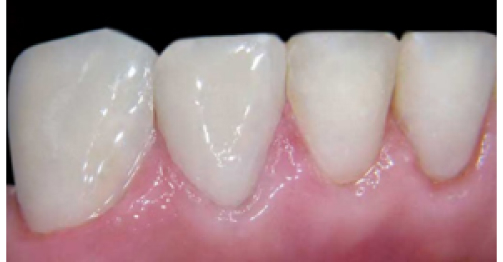
before
in work
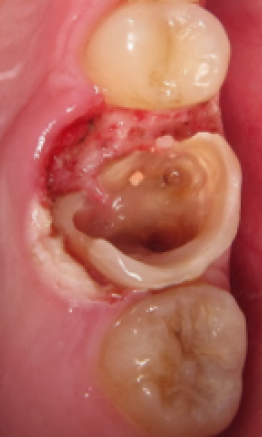
after
Grid metal composite is a combination of the composite material that works in compression and the metallic grid that works in tention. In case of tooth restoration with the use of the reinforced grid metal composite, disadvantages of the composite material are compensated for by advantages of the metallic grid. Such combination of materials allowed to open new directions in dentistry which were confirmed by scientific and long-term clinical results.
The mesh enables to repair major and total defects in the tooth crown, the dental row defects and restore most of the conventionally removed teeth.
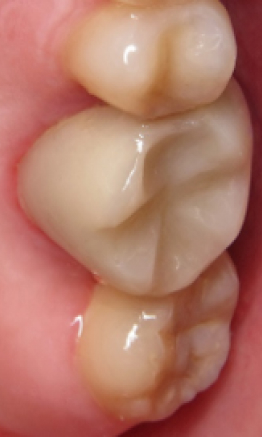
before
in work
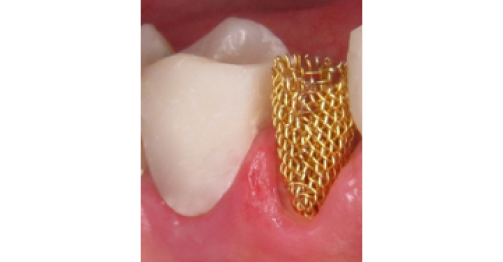
after
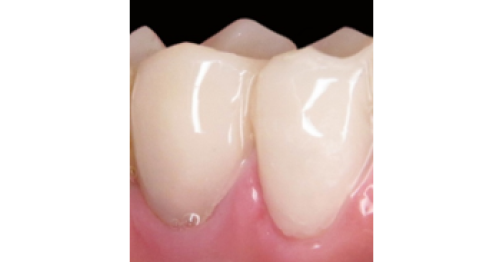
The reinforcement dentistry by Doctor M. Melikian is an atraumatic system for dental restoration/ reconstruction and prosthesis by reinforcement, which enables to eliminate the defects in solie tissues of teeth and the dental row using the mesh metallic composite.
The systematization of the frontal teeth defect elimination methods with a mesh metallic composite enabled us to create a classification.
The classification takes into account all possible (caries and non-caries) defects and their properties: localization, depth, and direction for the frontal teeth group. Between one and nine atraumatic defect elimination methods using mesh metallic composite are proposed for each of the nine defect classes. All methods are patented. The only exclusion is class 1 (the cutting edge is up to 2 mm) which is later to be discussed here. There is an option of the gentlest possible restoration/ reconstruction in elimination of defects of minimum 2 mm for restoration of teeth that are destroyed below the gingival level.
We developed and patented atraumatic methods of eliminating the pathological teeth abrasion using composite material and mesh metallic composite (MMC) material, which meet the MIPS concept (Minimal Invasion with Pulp Save) - the minimum invasion (MI) and pulp saving (PS) by M. Melikian. In 2009, the teeth abrasion classification was also proposed.
In 2009, the innovative technology was authorized by the Russian Federal Commission for Surveillance in Healthcare.
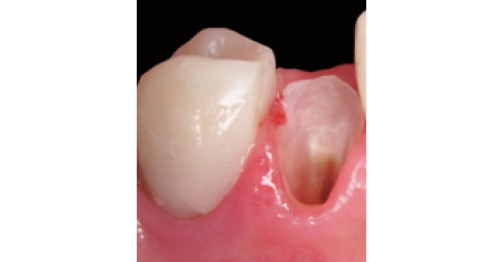
before
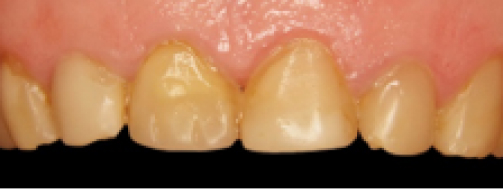
in work
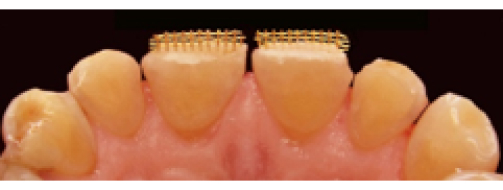
after
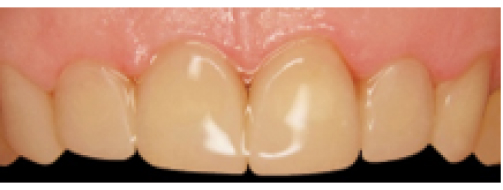
The technology is an efficient tool of orthopedic, treatment and surgical dentistry, orthodontics, implantology, periodontics, and pediatric dentistry.
Indications for use of the new medical technology
- Restoration of the tooth crown of the frontal teeth group using the reinforced and non-reinforced composite material by M. Melikian
- Restoration of the lateral dental groups with reinforcement by M. Melikian
- Tooth restoration using reinforcing posts made of gold-plated metallic mesh by M. Melikian
- Manufacturing of the mesh composite crown M. Melikian
- Manufacturing of reinforcing mesh and beam adhesive bridge-like prostheses M. Melikian
- Root perforation elimination in the region of bifurcation or trifurcation via reinforcement method by M. Melikian
- The repeated restoration of teeth crowns on the preserved stump via reinforcemet by M. Melikian
- Atraumatic methods of elimination of the generalized teeth abrasion via reinforcement method by M. Melikian
- Elimination of wedge-like teeth defects via teeth reinforcement method by M. Melikian
- Elimination of diastems and trems via teeth reinforcement method by M. Melikian
- Restoration of lateral dental groups in case of crown and root fractures via reinforcement method by M. Melikian
- Tooth splinting by M. Melikian reinforcement method
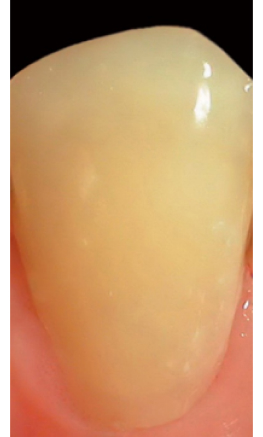
before

in work

after
The M. Melikian reinforcement method with composite materials offers numerous advantages: all manipulations are non invasive, preparation is carried out without anesthesia, teeth are not ground to match some particular structure; availability of the transformable and designable metal mesh matrix; light and solid metallic composite monolith structure; esthetic view and durability of restorations; complete restoration of the teeth morphology and functions; a possibility to eliminate any defects; restoration of conventionally removed teeth; preservation of teeth vitality; preservation of free access to channels; no preparation of intact teeth; no depulping of the support teeth; time saving, systemic approach and high efficacy.
before
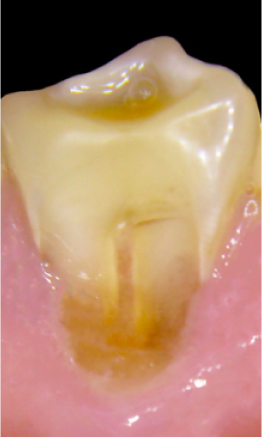
in work
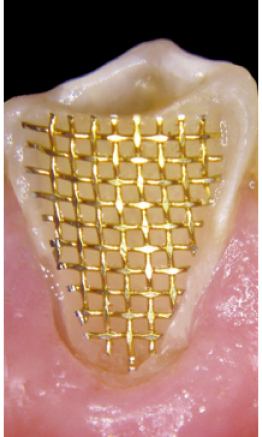
after
The clinical practice and scientific research indicate that the metallic gold-plated plexiform mesh is a multi-purpose one. It neither oxidizes nor destroys inside the composite material. After its introduction into the composite material, it minimizes the drawbacks of the latter.
Mesh:
- it increases the mechanical durability of the composite material and the service life of the reinforced restoration;
- it minimizes the polymerization stress and shrinkage
- it reduces the micro-leakage and recurrent caries;
- it improves the edge fitting of the composite material to the tooth solid tissues;
- in case of functional loads, it reduces and evenly distributes the tension in the composite restoration in the adhesion region (the region where the composite material connects with the solid tooth tissues);
- it prevents growth and occurrence of cracks in the reinforced area of the composite restoration;
- it prevent chips and splits off of the composite restoration
The above advantages increase the useful life of restored teeth.
The results of the the analysis of MMC durability properties indicated that the durability properties depend on the mesh location towards the load. The most appropriate location increases the maximum load by 75%.
before
in work
after
The mathematical modelling established that the use of the mesh reinforcement during the cutting edge restoration enables to reduce the maximum equivalent tensions in solid tooth tissues by 27.4 % (and along the dental axial line, by 37.0%) and to reallocate the tension from the affected area of the composite adhesion to a tooth to the middle third of the oral surface of the crown portion of the tooth being restored. 2 years after restoration of the cutting edge of teeth with the reinforced composite, 95.4% restorations were rated as excellent, 1.53%, as good, 3.07%, as satisfactory.
Complications, corresponding to unsatisfactory quality assessment (restoration fracture, etc.) were not found.
before
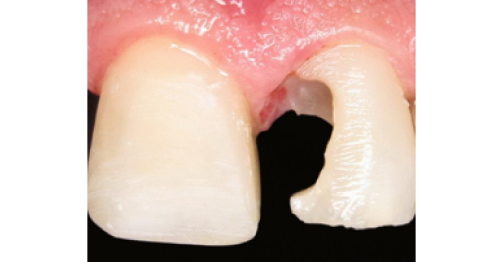
in work
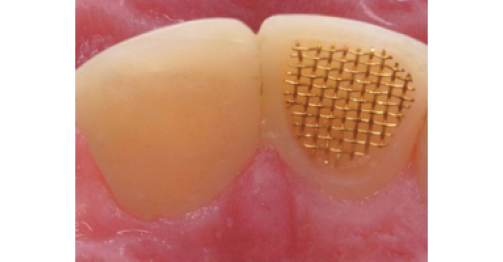
after
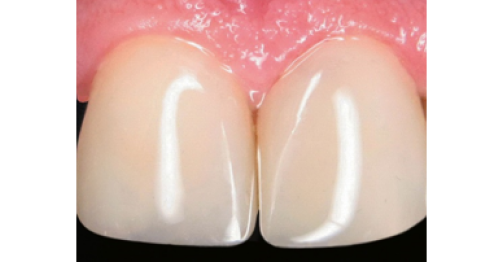
200+ atraumatic tooth treatment and prosthetics methods have been developed over 26 years and are successfully used in clinical practice. 100+ innovative methods are undergoing the clinical tests. The basic postulates of the clinical applications are scientifically substantiated. The developments were protected by the 71 Russian patents and two U.S. patents in 2002. The patenting is underway.
The technology is awarded with 10 gold medals at the international exhibitions of ideas, innovations and inventions in Germany, France, Belgium, Switzerland, South Korea, China, Kuwait, Ukraine. The golden medal was awarded in the Eurasian Economic Community for the Innovative Project at the Shanghai Forum. The order of the Kingdom of Belgium for the contribution to the innovative medicine. The anniversary, tenth, award was the Great Gold Medal "Leonardo da Vinci" of the European Academy of Sciences (Mougins, France, 2021). One thesis was defended and two theses were finalized on the technology.
before
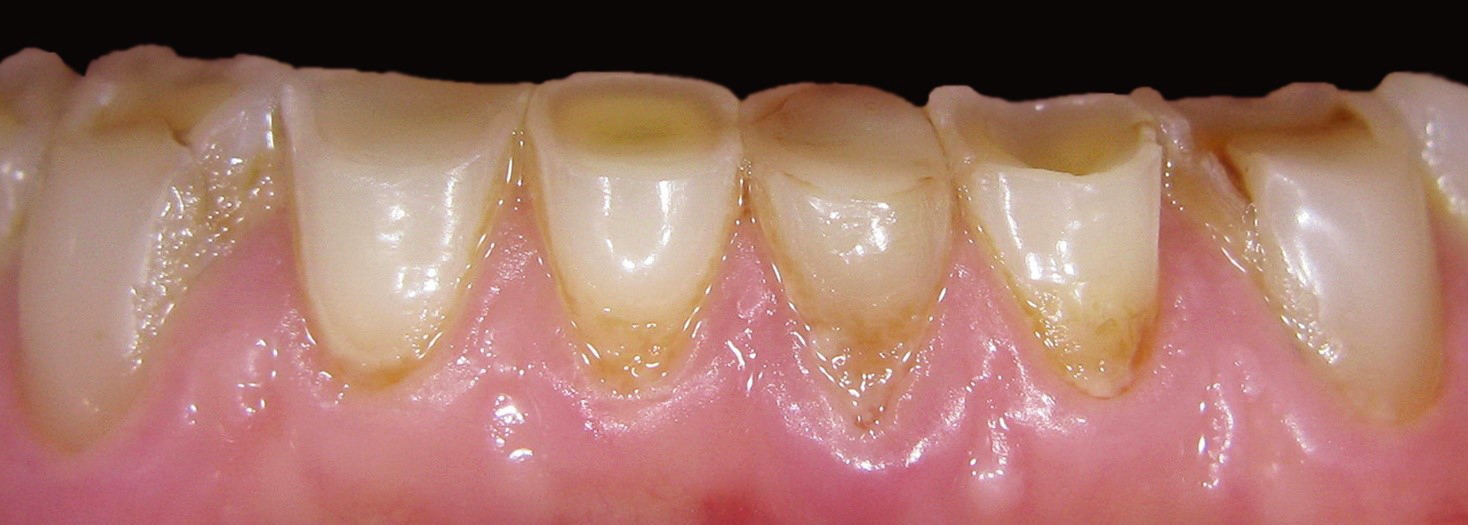
before
in work
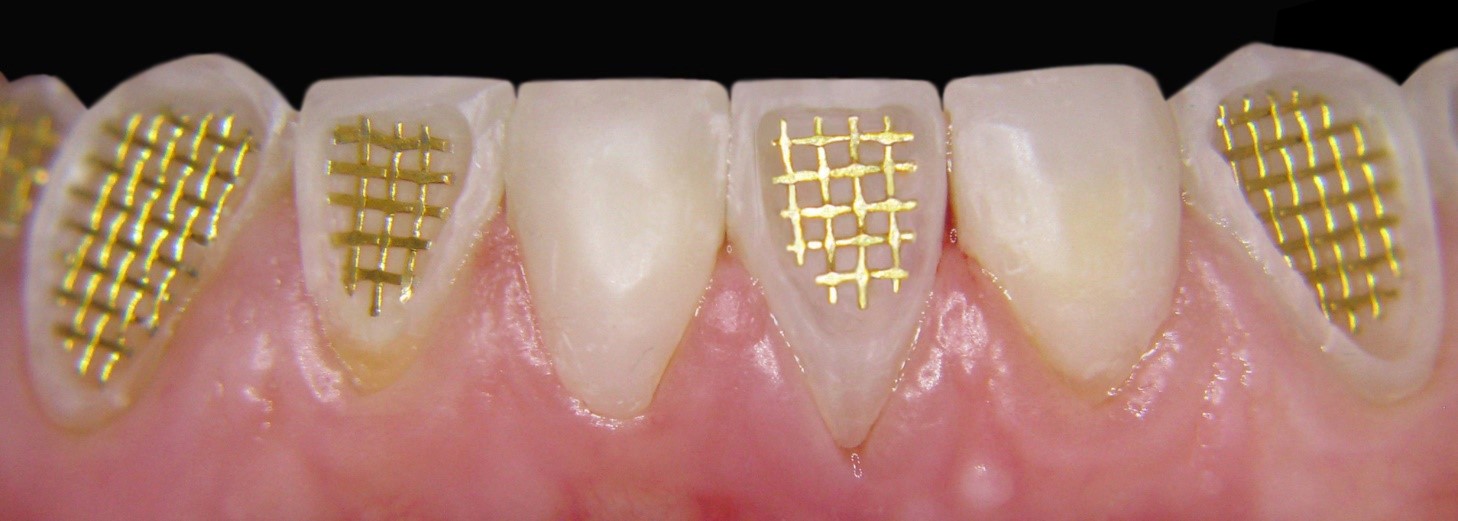
after